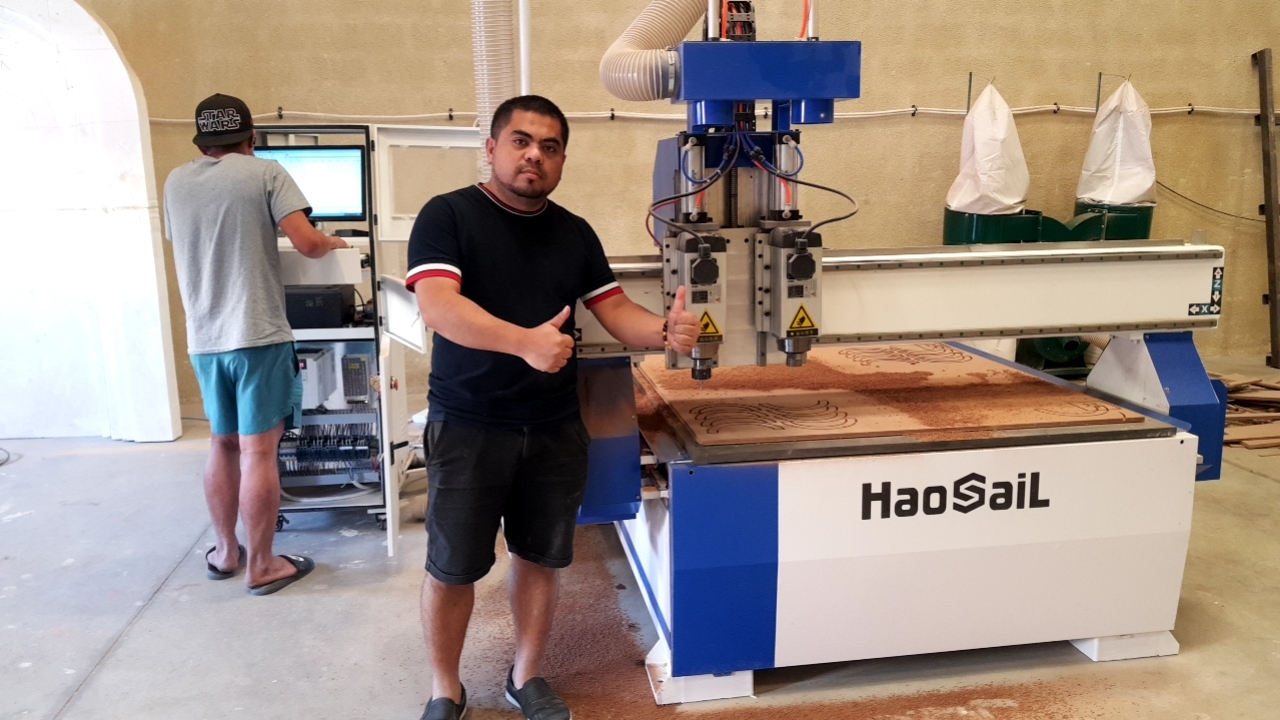
The CNC router is a versatile and precise machining tool widely used in woodworking, metalworking, and plastic fabrication. By combining computer numerical control (CNC) technology with high-speed cutting capabilities, the CNC router enables efficient production of intricate designs with exceptional accuracy. This article explores the working principles of CNC routers, essential safety precautions, and proper operation methods to maximize performance.
Working Principle of a CNC Router
1. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Integration
The CNC router operates based on digital designs created in CAD software. These designs are converted into machine-readable G-code, which dictates the tool’s movements.
2. Precision Motion Control
The CNC router uses servo or stepper motors to move the cutting tool along the X, Y, and Z axes with micron-level accuracy. This ensures clean cuts and consistent results.
3. Spindle and Cutting Tools
A high-speed spindle (typically 8,000–24,000 RPM) rotates cutting bits, such as end mills or engraving tools, to shape materials like wood, aluminum, or acrylic.
4. Vacuum or Mechanical Hold-Down
Many CNC routers feature vacuum tables or clamps to secure workpieces, preventing movement during machining.
5. Dust Extraction System
Built-in dust collectors or external vacuum systems remove debris, maintaining visibility and reducing health hazards.
Key Safety Precautions
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Always wear safety glasses, hearing protection, and dust masks when operating a CNC router. Avoid loose clothing or jewelry.
2. Tool Inspection
Check cutting tools for damage or wear before use. Dull or chipped bits can cause poor cuts or kickback.
3. Material Securement
Ensure the workpiece is firmly clamped or vacuum-sealed to prevent shifting during operation.
4. Emergency Stop Familiarity
Locate and test the CNC router’s emergency stop button before starting a job.
5. Dust Management
Regularly empty dust collection systems to prevent clogging and maintain airflow.
Operational Best Practices
1. Machine Calibration
- Verify the CNC router’s axis alignment and spindle perpendicularity.
- Perform a test run on scrap material to confirm tool paths.
2. Tool Selection and Setup
- Choose the appropriate bit for the material (e.g., straight bits for plywood, ball-nose bits for 3D carving).
- Set the correct feed rate and spindle speed to avoid burning or chipping.
3. Workpiece Zeroing
- Use the CNC router’s probe or manual method to establish the X, Y, and Z zero points.
- Double-check measurements to prevent misaligned cuts.
4. Monitoring the Process
- Observe the first few minutes of operation to ensure proper cutting.
- Pause if unusual vibrations or noises occur.
5. Post-Operation Maintenance
- Clean the CNC router’s bed, rails, and spindle after use.
- Lubricate linear guides and ball screws as recommended.
Advantages of Modern CNC Routers
- Precision: Achieve tolerances within ±0.1 mm.
- Speed: Complete complex designs faster than manual methods.
- Repeatability: Produce identical parts for batch processing.
- Versatility: Compatible with woods, plastics, composites, and soft metals.
Conclusion
The CNC router is a transformative tool for precision manufacturing, combining automation with high efficiency. By understanding its working principles, adhering to safety protocols, and following operational best practices, users can maximize productivity while minimizing risks. Whether for hobbyist projects or industrial production, mastering the CNC router ensures consistent, professional-quality results. Regular maintenance and proper tooling further extend the machine’s lifespan, making it a valuable investment for any workshop.
Final Tip: Always consult the CNC router’s manual for model-specific guidelines and keep software/firmware updated for optimal performance.