Mar 06, 2026

Aug 27, 2025

Aug 12, 2025

Jun 04, 2025
B4, Qingdao High-Tech Zone, No. 17 Songyuan Road, Qingdao.
+86 13864822549
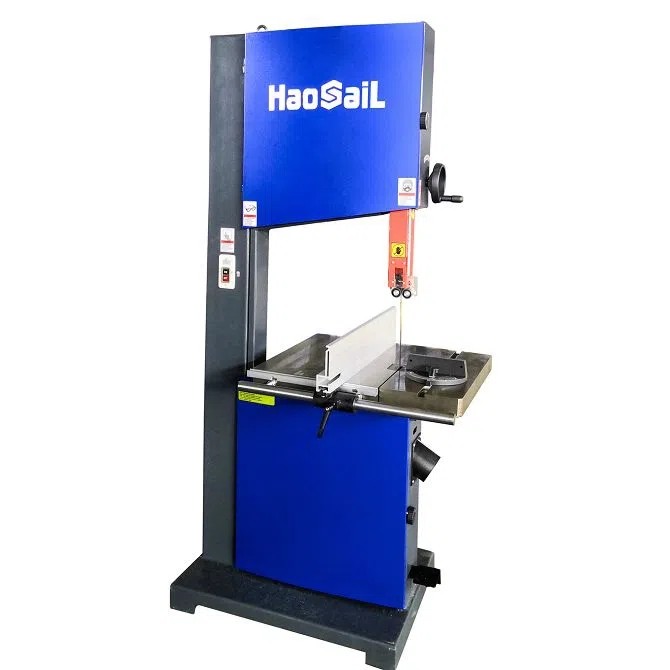

The woodworking band saw is an indispensable tool in modern woodshops, offering unparalleled versatility for cutting curves, resawing lumber, and creating intricate designs. This stationary power tool operates on a simple yet effective principle that has made it a staple for carpenters and furniture makers alike. Understanding how to properly use a woodworking band saw ensures both safety and optimal performance in your woodworking projects.
Working Principle
At its core, the woodworking band saw, toothed metal blade stretched between two or more wheels to cut material:
1. The blade rotates in a continuous loop, typically at speeds between 500-3,000 FPM
2. The workpiece is guided against the blade either freehand or using a fence/miter gauge
3. Cutting occurs as the downward-moving blade teeth engage with the wood fibers
Modern woodworking band saws feature:
- Adjustable blade speeds for different materials
- Blade tensioning mechanisms for precise cuts
- Tracking controls to keep the blade centered on the wheels
- Dust collection ports for cleaner operation
Safety Considerations
When operating a woodworking band saw, always prioritize safety:
1. Blade Guard Adjustment: Keep guards within 1/4" of the workpiece thickness
2. Push Stick Use: Always use push sticks for small pieces (under 3")
3. Eye Protection: Wear safety goggles to prevent sawdust injuries
4. Hearing Protection: The machine's noise levels often exceed 85 dB
5. Blade Selection: Match blade width to cutting radius (narrower blades cut tighter curves)
Proper Operation Techniques
To get the most from your woodworking band saw:
1. Machine Setup
- Ensure proper blade tension (should deflect about 1/4" when pressed)
- Adjust guides and bearings to just clear the blade
- Verify table is square to the blade for straight cuts
2. Cutting Procedures
- Mark cut lines clearly on the workpiece
- Feed material steadily without forcing
- For curves, rotate the workpiece smoothly against the blade
- Use relief cuts for tight curves to reduce blade binding
3. Maintenance Routines
- Clean sawdust buildup after each use
- Lubricate moving parts monthly
- Check blade condition regularly for tooth damage
- Inspect tires for wear and replace when grooved
Advanced Applications
The woodworking band saw excels at specialized tasks:
- Resawing: Cutting boards into thinner slabs
- Veneer Production: Creating thin wood slices
- Compound Cutting: Making angled cuts through thick stock
- Joinery Work: Crafting tenons and other joints
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even quality woodworking band saws may encounter problems:
- Blade Drift: Adjust blade tension or realign table
- Vibration: Check wheel balance and machine bolts
- Burn Marks: Clean blade or reduce feed rate
- Premature Blade Wear: Verify proper tension and speed settings
Conclusion
The woodworking band saw remains one of the most versatile tools in any woodshop, capable of handling everything from rough lumber processing to delicate scrollwork. By understanding its operating principles, respecting its safety requirements, and mastering proper techniques, woodworkers can unlock its full potential. Regular maintenance ensures years of reliable service, while proper blade selection and machine adjustments guarantee precision cuts. Whether you're a professional cabinetmaker or a weekend hobbyist, investing time to learn your woodworking band saw thoroughly will pay dividends in the quality and efficiency of your work. Always remember that like all power tools, the band saw demands respect - its incredible cutting ability comes with responsibility for safe operation.